Features Correlation
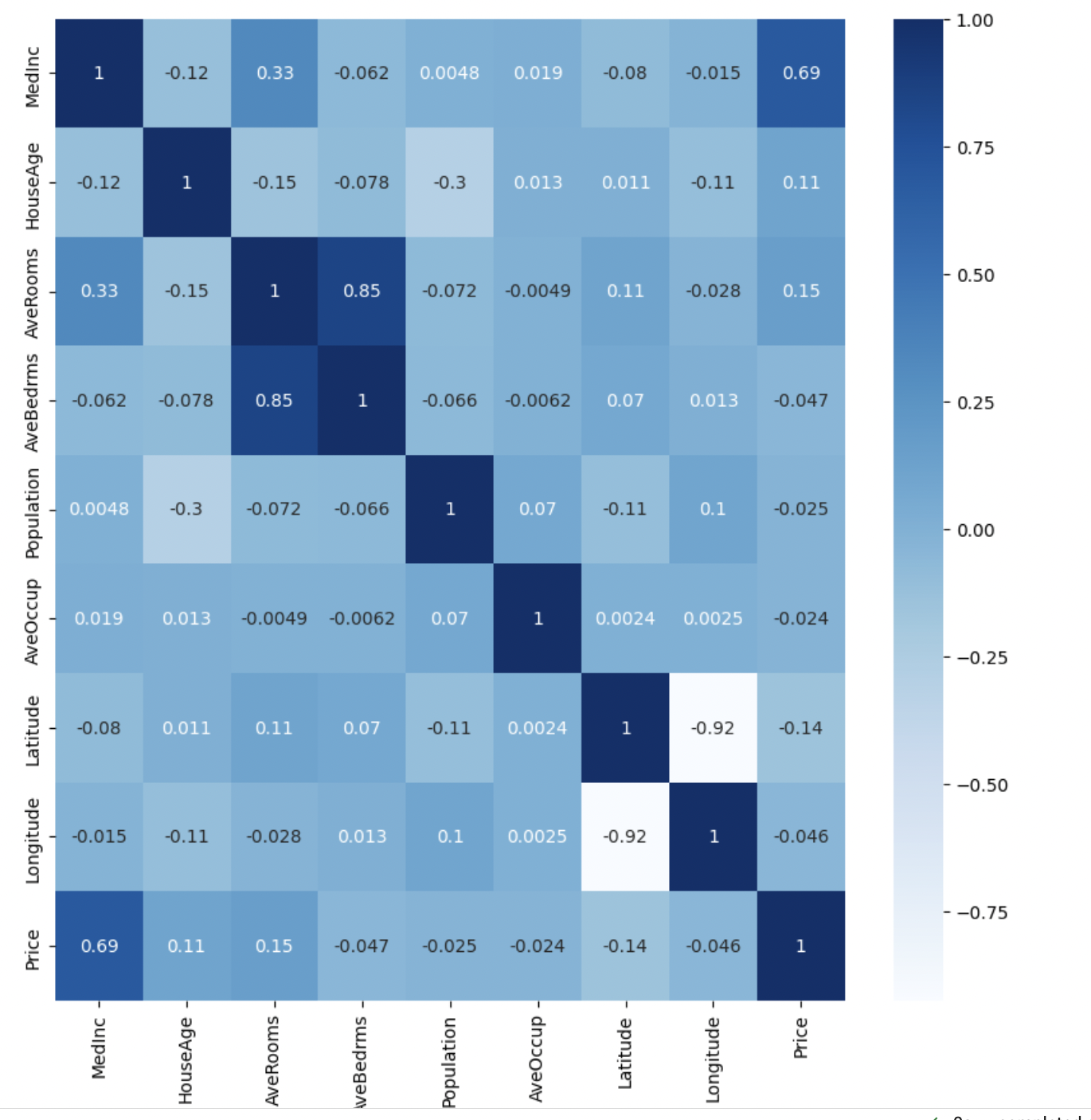
Analyzing the correlations, we can observe the following insights:
- Median Income (MedInc): shows a relatively strong positive correlation (0.688) with the Price. This suggests that higher median income tends to be associated with higher housing prices.
- House Age (HouseAge): has a weak positive correlation (0.106) with the Price. This indicates that, to some extent, older houses may have slightly higher prices.
- Average Number of Rooms (AveRooms): exhibits a moderate positive correlation (0.152) with the Price. This implies that houses with more rooms tend to have higher prices.
- Average Number of Bedrooms (AveBedrms): has a weak negative correlation (-0.047) with the Price. This suggests that an increase in the number of bedrooms is associated with a slight decrease in housing prices.
- Population and Average Occupancy (Population, AveOccup): show weak correlations (both positive and negative) with the Price. These features have minimal influence on housing prices.
- Latitude and Longitude: exhibit weak correlations with the Price (-0.144 and -0.046, respectively). These geographic coordinates have a slight negative influence on housing prices, indicating that certain areas may have slightly lower prices.