Correlation Features
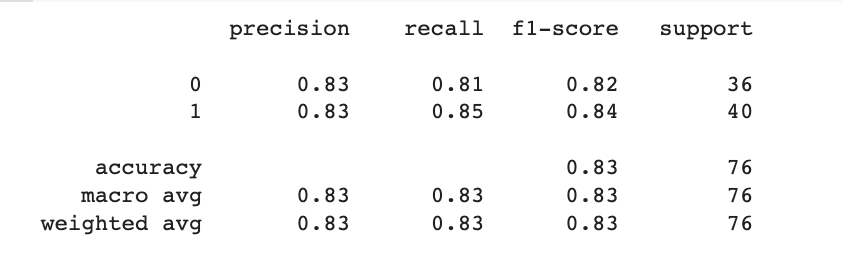
The correlation matrix provides insights into the relationships between different features and the target variable (heart disease). Here is a summary of the observations:
- Age (age) has a weak negative correlation (-0.225) with the target variable. As age increases, the likelihood of heart disease tends to decrease slightly.
- Sex (sex) has a moderate negative correlation (-0.281) with the target variable. Being male is associated with a slightly higher probability of heart disease.
- Chest pain type (cp) shows a moderate positive correlation (0.434) with the target variable. Higher chest pain type values are indicative of a higher probability of heart disease.
- Resting blood pressure (trestbps), cholesterol levels (chol), and fasting blood sugar (fbs) have weak correlations with the target variable. They do not appear to have a significant impact on heart disease prediction.
- Resting electrocardiographic results (restecg) and exercise-induced angina (exang) have weak to moderate correlations with the target variable. They contribute to the prediction of heart disease but to a lesser extent compared to other features.