Classification Report:
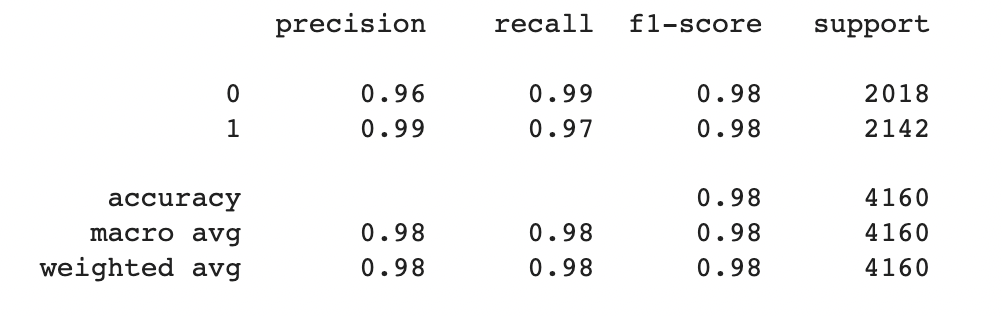
- Precision: For class 0 (real news), the precision is 0.96, indicating that 96% of the news articles predicted as real are actually real. For class 1 (fake news), the precision is 0.99, meaning that 99% of the news articles predicted as fake are indeed fake. High precision values suggest a low false positive rate, indicating that the model is effective in correctly identifying real and fake news.
- Recall: The recall for class 0 is 0.99, indicating that the model correctly identifies 99% of the actual real news articles. The recall for class 1 is 0.97, suggesting that the model correctly identifies 97% of the actual fake news articles. High recall values indicate a low false negative rate, showing that the model can effectively capture most of the real and fake news articles.
- F1-score: The F1-score is the harmonic mean of precision and recall and provides a balanced measure of the model's performance. The F1-score for both classes is 0.98, indicating a good balance between precision and recall and an overall strong performance of the model.
- Support: The support represents the number of instances for each class. In this case, there are 2018 instances of real news (class 0) and 2142 instances of fake news (class 1).
- Accuracy: The overall accuracy of the model is 0.98, suggesting that it correctly predicts 98% of the news articles in the dataset.
Based on the classification report, the model shows high precision, recall, and F1-score values for both real and fake news classes. The accuracy of 98% indicates that the model performs well in classifying news articles as real or fake. However, it is essential to consider other evaluation metrics and conduct further analysis to ensure the model's robustness and generalizability.