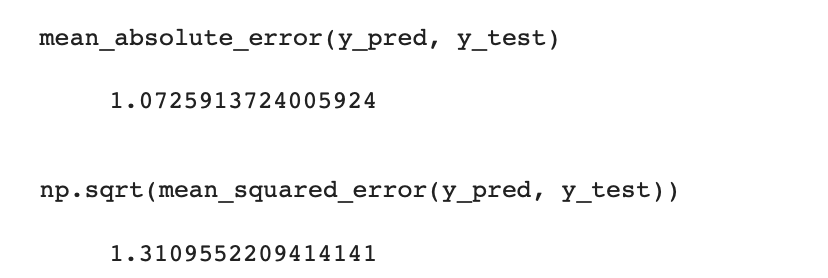
For the linear regression model, the mean absolute error (MAE) is calculated as 1.0726. This means that, on average, the predicted car prices deviate from the actual prices by approximately 1.0726 lakhs. The MAE measures the average absolute difference between the predicted and actual values, without considering the direction of the errors.
The root mean squared error (RMSE) is computed as 1.3110. This metric represents the square root of the average of the squared differences between the predicted and actual values. The RMSE provides a measure of the typical magnitude of the errors made by the model. In this case, the RMSE indicates that the predicted car prices, on average, deviate by approximately 1.3110 lakhs from the actual prices.
Both the MAE and RMSE are used to assess the accuracy and precision of the linear regression model's predictions. A lower MAE and RMSE indicate better performance, as they imply smaller differences between the predicted and actual values. However, the interpretation of these metrics depends on the specific context and the scale of the target variable.
The root mean squared error (RMSE) is computed as 1.3110. This metric represents the square root of the average of the squared differences between the predicted and actual values. The RMSE provides a measure of the typical magnitude of the errors made by the model. In this case, the RMSE indicates that the predicted car prices, on average, deviate by approximately 1.3110 lakhs from the actual prices.
Both the MAE and RMSE are used to assess the accuracy and precision of the linear regression model's predictions. A lower MAE and RMSE indicate better performance, as they imply smaller differences between the predicted and actual values. However, the interpretation of these metrics depends on the specific context and the scale of the target variable.
